In the realm of dental restorations, the Zirconia Dental Bridge stands out as a significant advancement. A Zirconia Bridge is a type of dental prosthesis made from zirconium dioxide, a durable and aesthetically pleasing material. This type of bridge is used to replace one or more missing teeth, providing both functional and cosmetic benefits. Its importance in dental restoration cannot be overstated, as it offers a robust solution for both anterior and posterior teeth.
1.What is a Zirconia Bridge?
A Zirconia Dental Bridge is a dental prosthesis made primarily from zirconium dioxide, a high-strength ceramic material. Zirconia is renowned for its exceptional durability and biocompatibility, making it an ideal choice for dental restorations. The material is often preferred for its ability to blend seamlessly with natural teeth, providing a realistic and aesthetically pleasing appearance. Unlike traditional metal-based bridges, Zirconia Bridges eliminate the risk of metal allergies and unsightly gray lines at the gum margin.
The use of zirconia in dentistry has evolved significantly over the years. Initially used in orthopedics for hip replacements due to its strength and biocompatibility, zirconia eventually found its way into dental applications in the early 2000s. The development of computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technology has further advanced the precision and efficiency of creating Zirconia Bridges. This technological innovation has enabled dentists to design and fabricate highly accurate and custom-fit dental restorations.
2.Advantages of Zirconia Bridges
Durability and Strength
One of the primary advantages of a Zirconia Dental Bridge is its remarkable durability and strength. Zirconia is known for its high fracture resistance, making it an excellent choice for both anterior and posterior dental restorations. This material can withstand the significant biting forces in the mouth without chipping or cracking, ensuring longevity and reliability. Furthermore, the robust nature of zirconia makes it suitable for patients who grind their teeth or have a strong bite.
Aesthetic Appeal
Zirconia Bridges offer superior aesthetic benefits compared to traditional metal-ceramic bridges. The translucent nature of zirconia allows it to mimic the optical properties of natural teeth, providing a seamless blend with the surrounding dentition. This makes zirconia particularly advantageous for restoring front teeth, where appearance is crucial. Additionally, zirconia can be color-matched to existing teeth, ensuring a harmonious and natural-looking smile.
Biocompatibility
Zirconia is highly biocompatible, which means it is well-tolerated by the body and does not cause adverse reactions. This property significantly reduces the risk of allergic reactions and gum irritation, which can be a concern with metal-based bridges. The use of zirconia also promotes healthy gum tissue, as it does not contribute to inflammation or bacterial growth. This makes Zirconia Bridges a safe and comfortable option for long-term dental restorations.
3.The Manufacturing Process of Zirconia Bridges
CAD/CAM Technology
The advent of CAD/CAM technology has revolutionized the production of Zirconia Dental Bridges. CAD (Computer-Aided Design) allows dentists and dental technicians to create precise digital models of the patient's teeth. These digital models are then used to design the Zirconia Bridge with exact specifications. Once the design is finalized, CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) technology takes over, using milling machines to carve the bridge from a solid block of zirconia. This process ensures high accuracy and a custom fit for each patient.
Step-by-Step Manufacturing Process
Digital Scanning: The first step involves taking a digital impression of the patient's mouth using an
intraoral scanner.
Design: The scanned data is used to create a 3D digital model of the Zirconia Bridge using specialized CAD software. Adjustments can be made to ensure proper fit and function.
Milling: The digital design is sent to a CAM machine, which mills the bridge from a pre-sintered
zirconia block. This step requires high precision to achieve the desired shape and dimensions.
Sintering: The milled bridge undergoes a sintering process, where it is heated to a high temperature to achieve its final strength and hardness.
Finishing and Polishing: The bridge is then polished and, if necessary, stained to match the natural color of the patient's teeth. This ensures a smooth surface and an aesthetically pleasing appearance.
Fitting and Adjustment: Finally, the Zirconia Bridge is tested in the patient's mouth to ensure a proper fit. Any necessary adjustments are made before it is permanently cemented in place.
4.Indications for Zirconia Bridges
Suitable Cases
Zirconia Dental Bridges are versatile and can be used in various dental restoration scenarios. Some common indications for their use include:
Single Missing Tooth: Zirconia Bridges are an excellent option for replacing a single missing tooth, particularly in the front teeth where aesthetics are crucial.
Multiple Missing Teeth: They can also be used to replace multiple adjacent missing teeth, providing a durable and cohesive restoration.
Posterior Teeth: Due to their high strength, Zirconia Bridges are suitable for restoring posterior teeth, where biting forces are greater.
Patients with Metal Allergies: Individuals who are allergic to metals used in traditional bridges can benefit from the biocompatibility of zirconia.
Limitations and Contraindications
While Zirconia Bridges offer numerous benefits, there are certain situations where they may not be the best choice:
Severe Bruxism: In cases of severe teeth grinding (bruxism), although zirconia is strong, excessive grinding can still cause wear.
Insufficient Tooth Structure: If there is not enough tooth structure to support the bridge, alternative treatments may be considered.
Poor Oral Hygiene: Zirconia Bridges require good oral hygiene to prevent complications. Patients with poor oral hygiene habits may face increased risks of failure.
5.Maintenance and Care of Zirconia Bridges
Daily Oral Hygiene
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for the longevity of a Zirconia Dental Bridge. Here are some essential daily care tips:
Brushing: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and non-abrasive toothpaste to brush your teeth at least twice a day. Pay special attention to the areas around the bridge to remove plaque and food particles.
Flossing: Floss daily using dental floss or interdental brushes to clean between the teeth and under the bridge. Proper flossing helps prevent gum disease and cavities around the bridge.
Mouthwash: Rinse with an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce bacterial load and maintain oral health.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are essential to ensure the health of both the Zirconia Bridge and the surrounding teeth and gums. During these visits, your dentist will:
Professional Cleaning: Perform professional cleanings to remove tartar and plaque that cannot be eliminated by regular brushing and flossing.
Inspection: Examine the bridge and supporting teeth for any signs of wear, damage, or decay.
Adjustments: Make any necessary adjustments to the bridge to ensure a perfect fit and function.
Long-term Maintenance
Zirconia Bridges are designed for durability, but proper care can further extend their lifespan:
Avoid Hard Foods: Although zirconia is strong, it is advisable to avoid biting on extremely hard foods, which could potentially damage the bridge.
Monitor Changes: Be aware of any changes in your bite or discomfort around the bridge area and report these to your dentist immediately.
Lifestyle Habits: Reduce habits such as nail-biting or using teeth to open packages, as these can exert excessive force on the bridge.
6.Comparison of Zirconia Bridges with Other Dental Bridges
Metal-Ceramic Bridges
Aesthetics: Zirconia Bridges provide a more natural, tooth-like appearance due to their translucency, whereas metal-ceramic bridges may show a gray line at the gum margin over time.
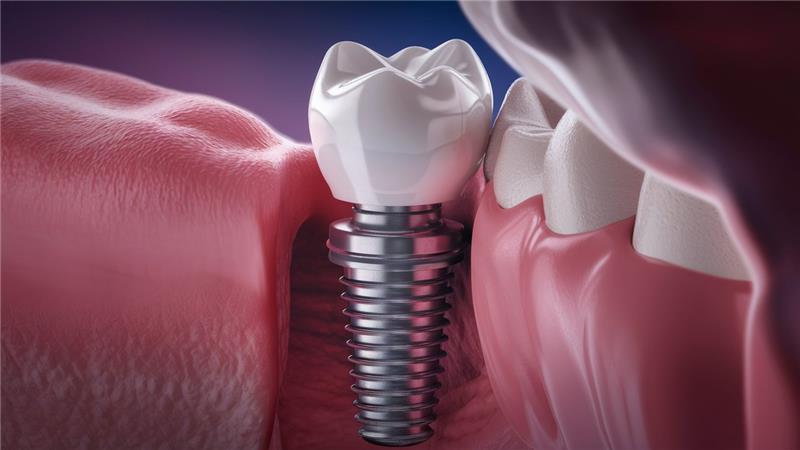
Durability: Both are durable, but zirconia has higher fracture resistance, making it ideal for strong bites and posterior teeth.
Biocompatibility: Zirconia is highly biocompatible, reducing the risk of allergic reactions and gum irritation compared to metal-ceramic bridges.
All-Ceramic Bridges
Aesthetics: Both offer excellent aesthetics, but zirconia's strength allows it to be used in posterior regions without compromising appearance.
Strength: Zirconia Bridges are stronger and more durable than other all-ceramic options, making them suitable for high-bite-force areas.
Cost: Zirconia Bridges can be more expensive due to advanced materials and technology, but their long-term benefits often justify the cost. [Insert internal link: Zirconia bridge price - product category page]
Common Questions and Answers (FAQ)
What is the Cost of a Zirconia Bridge?
The cost of a Zirconia Dental Bridge can vary based on several factors, including the complexity of the case, the number of teeth being replaced, and the geographic location of the dental practice. Generally, zirconia bridges tend to be more expensive than traditional metal-ceramic bridges due to the advanced materials and technology involved in their production. However, the durability, aesthetics, and biocompatibility of zirconia often justify the higher cost. [Insert internal link: Zirconia bridge price - product category page]
Is the Installation Process Painful?
The installation of a Zirconia Bridge typically involves minimal discomfort. The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia, which numbs the area and prevents pain during the process. Some patients might experience mild discomfort or sensitivity after the anesthesia wears off, but this is generally temporary and can be managed with over-the-counter pain medications.
What Are the Long-Term Effects?
Zirconia Bridges are designed for long-term use and have a high success rate. They are durable and can last many years with proper care and maintenance. The biocompatibility of zirconia also reduces the risk of gum irritation and allergic reactions, promoting healthier surrounding tissues. However, like all dental restorations, regular check-ups and good oral hygiene are crucial to ensure their longevity and function.
Are There Any Potential Problems with Zirconia Bridges?
While Zirconia Bridges are highly durable and reliable, there can be potential issues, such as:
Minor Adjustments: Sometimes, small adjustments may be necessary to ensure a perfect fit.
Wear on Opposing Teeth: Due to its hardness, zirconia can sometimes cause wear on the opposing natural teeth if the bite is not properly adjusted.
Initial Sensitivity: Some patients may experience initial sensitivity after the bridge is placed, but this typically subsides within a few days.
By consulting with a qualified dental professional and adhering to recommended care practices, most of these issues can be effectively managed.

