Understanding Dental Milling Machine Prices
2024-07-07
2024-08-13
The Complete Guide to digital scanning dental for Dentists
Digital scanning technology has significantly transformed the dental industry, bringing a multitude of benefits to both practitioners and patients. This technological advancement has enabled dentists to achieve higher precision in diagnostics and treatment planning, ultimately enhancing patient care. Digital scanning has evolved rapidly over the past few years, offering improved accuracy, speed, and ease of use. Its impact on dental practices is profound, streamlining workflows, reducing turnaround times, and elevating the standard of care.
1. What is Digital Scanning in Dentistry?
Digital scanning in dentistry refers to the use of advanced imaging technology to capture detailed three-dimensional (3D) representations of the oral cavity. Unlike traditional dental impressions, which require physical molds to create models of a patient's teeth and gums, digital scanning utilizes electronic sensors and software to generate accurate 3D models.
Basic Concept:
Digital scanning employs devices such as intraoral scanners, dental impression scanners, and 3D tooth scanners to capture precise data of the oral structures. These scanners use a combination of optical and laser technologies to scan the surfaces of teeth and gums, creating a detailed digital map.
How Digital Scanners Work:
Intraoral scanners are handheld devices used directly within the patient's mouth to capture 3D images. They are commonly utilized for creating digital impressions for crowns, bridges, and orthodontic appliances.
Dental impression scanners are used to digitize traditional physical impressions. This is particularly useful for dentists who are transitioning from traditional to digital workflows.
3D tooth scanners provide highly detailed images of individual teeth, which can be used for various dental procedures, including restorations and orthodontics.
Comparison with Traditional Dental Impressions:
Accuracy: Digital scans are more precise than traditional molds, reducing the risk of errors and the need for retakes.
Patient Comfort: Digital scanning is non-invasive and eliminates the discomfort associated with traditional impression materials.
Efficiency: Digital workflows are faster, allowing for quicker turnaround times in the production of dental restorations and appliances.
Storage and Transfer: Digital files are easy to store, share, and transfer, facilitating collaboration between dental professionals and labs.
2. Applications of Digital Scanning in Dentistry
Digital scanning technology has a wide range of applications in dentistry, significantly enhancing the precision and efficiency of various dental procedures. Below are some key areas where digital scanning is making a notable impact:
Restorative Dentistry:
Digital scanning is extensively used in restorative dentistry to design and fabricate crowns, bridges, inlays, and onlays. The use of an intraoral scanner allows dentists to capture highly accurate impressions of the prepared tooth, which can be directly sent to a dental lab for the fabrication of restorations.
Orthodontics:
In orthodontics, digital scanning creates precise 3D models of a patient's teeth, essential for planning and executing treatments such as braces and clear aligners. This technology provides a clear and accurate representation of the dental arches, allowing for precise treatment planning.
Implantology:
Digital scanning aids in the planning and placement of dental implants. Detailed images of the edentulous area and adjacent teeth obtained using a dental impression scanner are used to plan the optimal placement of implants.
General Dentistry:
In routine dental check-ups and diagnostics, intraoral scanners can quickly and accurately capture the current state of a patient's oral health, aiding in early detection of issues such as cavities and gum disease.
3. Types of Digital Scanning Equipment
The market for digital scanning equipment in dentistry is diverse, offering a range of devices designed to meet different clinical needs. Here are the primary types of digital scanners and their characteristics:
Intraoral Scanners:
Intraoral scanners are handheld devices used directly in the patient's mouth to capture 3D images of the teeth and gums. They are highly valued for their precision and ease of use.
Key Features:
High accuracy and resolution
Real-time scanning and visualization
Comfortable for patients
Ideal for capturing detailed images for crowns, bridges, and orthodontic appliances
Example Products:
Yucera YRC-02: Known for its high accuracy and user-friendly interface.
Medit i700: Offers fast scanning speeds and lightweight design.
Link to Intraoral Scanner: intraoral scanner
Dental Lab Scanners:
Dental lab scanners are designed for use in dental laboratories to scan physical dental impressions or models. They help convert traditional impressions into digital formats, facilitating the digital workflow.
Key Features:
High precision and ability to scan a variety of materials
Suitable for large-scale dental lab operations
Provides detailed data for prosthetics and complex restorations
Example Products:
Yucera RS300: Known for its high resolution and rapid scanning capabilities.
3Shape E4: Offers exceptional speed and accuracy for detailed scans.
Link to Dental Lab Scanner: dental lab scanner
3D Tooth Scanners:
3D tooth scanners focus on capturing detailed images of individual teeth, useful for various dental procedures like restorations and orthodontics.
Key Features:
Provides highly detailed and magnified images of teeth
Useful for diagnosing cracks, cavities, and other tooth-specific issues
Enhanced visualization for treatment planning
4. Advantages and Challenges of Digital Scanning
Advantages:
Enhanced Accuracy: Digital scanners, like the intraoral scanner, provide superior precision, reducing errors and ensuring better-fitting restorations.
Improved Patient Experience: Digital scanning is more comfortable than traditional impressions, eliminating the need for impression trays and materials.
Workflow Efficiency: Digital scanning streamlines workflows, allowing immediate data capture and quicker turnaround times.
Better Communication: Detailed digital images aid in patient understanding and facilitate professional collaboration.
Challenges:
High Initial Investment: The cost of purchasing and maintaining digital scanning equipment can be significant.
Learning Curve: Adopting new technology requires training and adjustment.
Technology Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility with existing systems can be challenging.
Data Security: Digital data storage raises concerns about security and privacy.
With these advantages and challenges in mind, dental professionals can make informed decisions about integrating digital scanning into their practices, enhancing both patient care and operational efficiency.
5. Choosing the Right Digital Scanning Equipment
Selecting the right digital scanning equipment for your dental practice involves careful consideration of various factors. Here are some guidelines to help you make an informed decision:
a. Assess Your Needs:
Determine the specific applications for which you will use the digital scanner. Whether it’s for general dentistry, orthodontics, implants, or restorative work, understanding your needs will guide you in selecting the appropriate device.
b. Budget Considerations:
Evaluate your budget for purchasing and maintaining the equipment. Digital scanners can range widely in price, so it's crucial to find a balance between cost and functionality.
c. Features and Capabilities:
Look for scanners with features that meet your clinical requirements. Important features to consider include accuracy, speed, ease of use, and compatibility with your existing systems.
d. Brand and Model Recommendations:
Here are some notable brands and models:
Yucera YRC-02 (Intraoral Scanner):
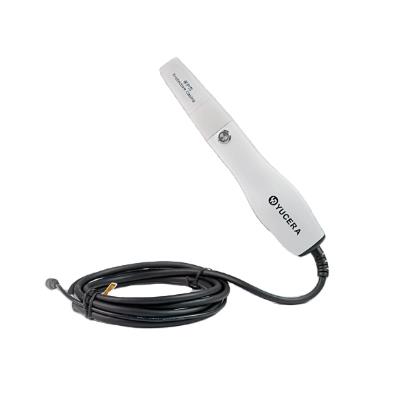

Known for its high accuracy and user-friendly interface.
Ideal for capturing detailed images for crowns, bridges, and orthodontic appliances.
Medit i700 (Intraoral Scanner):
Offers fast scanning speeds and lightweight design.
Suitable for routine dental diagnostics and complex procedures.
Link to Intraoral Scanner: intraoral scanner
Yucera RS300 (Dental Lab Scanner):

High resolution and rapid scanning capabilities.
Perfect for large-scale dental lab operations and detailed restorations.
3Shape E4 (Dental Lab Scanner):
Exceptional speed and accuracy for detailed scans.
Suitable for diverse dental materials and complex prosthetics.
Link to Dental Lab Scanner: dental lab scanner
e. Support and Training:
Consider the availability of customer support and training. Reliable technical support and comprehensive training can significantly ease the transition to digital workflows.
f. Future-Proofing:
Choose equipment that can adapt to future advancements in dental technology. Investing in upgradable systems can ensure your practice remains at the cutting edge.
6. Future Trends in Digital Scanning Technology
a. Artificial Intelligence Integration:
AI will increasingly assist in diagnostics and treatment planning, improving accuracy and efficiency.
b. Cloud-Based Solutions:
Cloud storage and processing will enhance data accessibility and facilitate remote consultations.
c. Enhanced Imaging Technologies:
Future scanners will offer higher resolution and faster scanning speeds, improving diagnostic capabilities.
d. Mobile and Portable Scanners:
Portable devices will make digital scanning more accessible, extending advanced dental care to a wider range of settings.
e. 3D Printing Integration:
Combining digital scanning with 3D printing will streamline the production of dental prosthetics and appliances, reducing turnaround times.