A Comprehensive Guide to Digital Dental Solutions
2024-07-02
2024-10-14
The main difference between digital and traditional dental materials lies in their processing methods and precision. Digital materials typically utilize Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) technologies for precise cutting and shaping, while traditional materials, such as composite resins and metal alloys, rely more on manual operations.
Precision and Consistency: Digital materials ensure a precise fit and function of the restorations through CAD/CAM technologies, reducing clinical errors and enhancing the accuracy of the restorations.
Aesthetic Outcomes: Digital materials can be matched to the patient's tooth color and achieve natural and aesthetic restorations through fine processing techniques. Particularly for anterior teeth and other areas with high aesthetic demands, digital materials can provide more realistic aesthetic effects.
Production Efficiency: With CAD/CAM technology, dental appliances such as crowns, bridges, and dentures can be rapidly manufactured, significantly reducing treatment time and improving production efficiency.
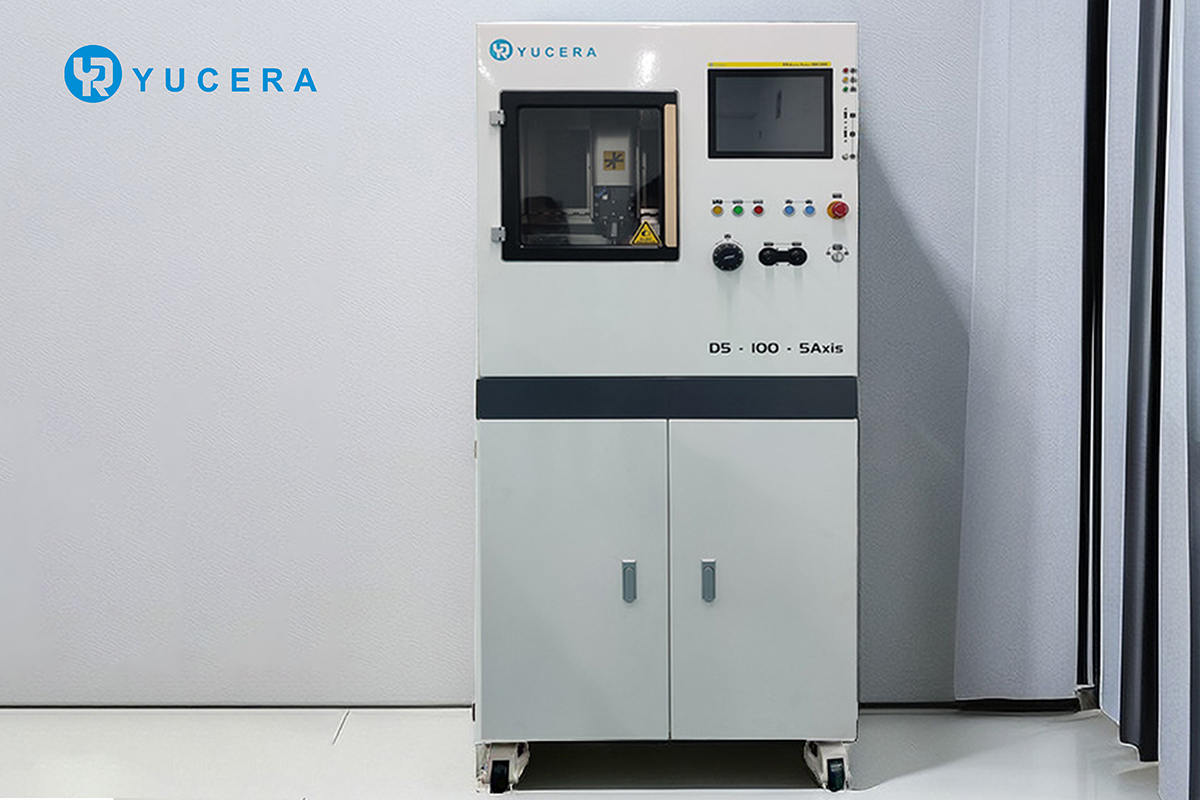

Material Waste Reduction: Digital processing technologies like CNC milling and 3D printing use materials precisely according to the required shape of the restoration, reducing material waste and thus lowering material costs.
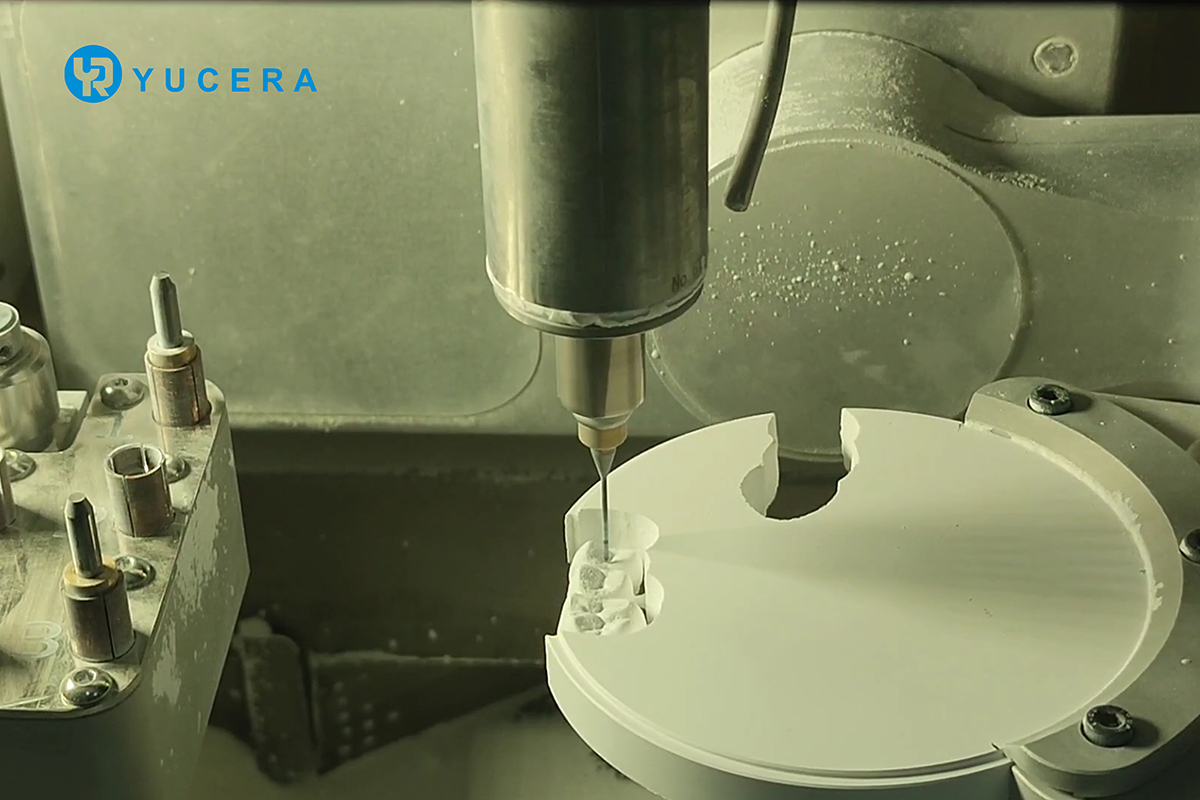

Biocompatibility: Digital materials generally have good biocompatibility, reducing patients' allergic reactions to materials and enhancing the safety of treatment.
Simplified Clinical Procedures: Digital impression technologies (such as intraoral scanning) simplify clinical procedures, reduce the number of patient visits, and provide a more friendly diagnostic and treatment experience.
Data Integration and Analysis: Digital materials and technologies support the integration of a large amount of data, facilitating deeper analysis and research to continuously improve material performance and clinical application effects.
Environmental Friendliness: Digital processing methods have high raw material utilization rates and are environmentally friendly, offering advantages in mass production. For example, digital impressions capture and store patient oral data on computers, resulting in no waste. Traditional impressions use plastic trays and excess plaster, which ultimately end up in landfills.
In summary, digital dental materials are gradually transforming the face of the dental industry by offering higher precision, better aesthetic effects, greater production efficiency, lower material waste, and environmental friendliness.